“Sky Birds, February 1935″ by C.B. Mayshark
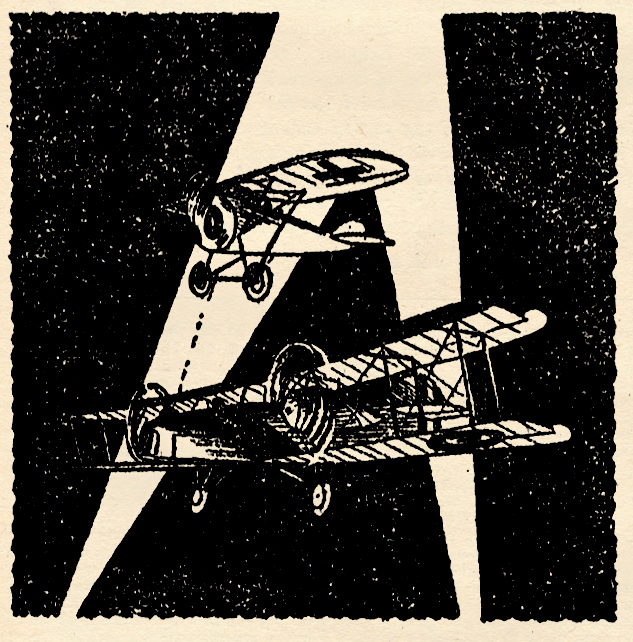
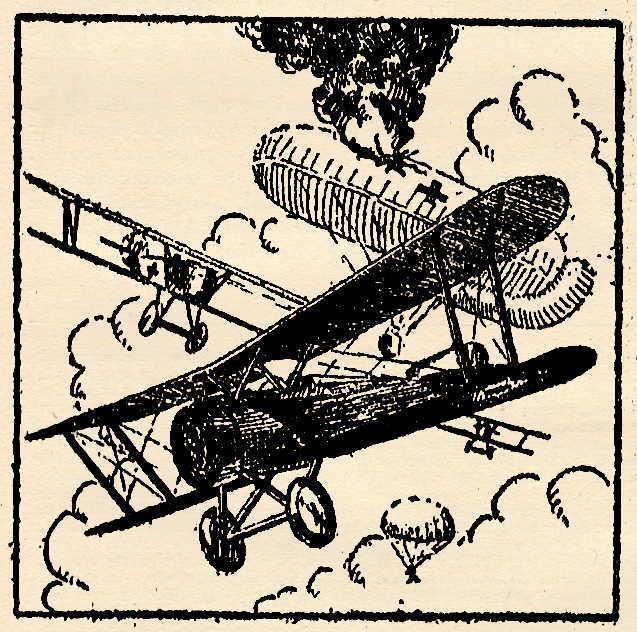
THIS May we’re celebrating the genius that is C.B. Mayshark! Mayshark took over the covers duties for Sky Birds with the July 1934 and would paint all the remaining covers until it’s last issue in December 1935. At the start of his run, Sky Birds started featuring a different combat maneuver of the war-time pilots. The lower corner presenting a play-by-play of that month’s maneuver with the remainder of the cover illustrating it. For February 1935 issue Mayshark gives us “Safety In Numbers!”
Combat Maneuvers of War-Time Pilots:
Safety In Numbers
UNDER ordinary circumstances,  when you get one ship in combat with many, you have a very one-sided battle. Of course, there were instances during the war when a single combatant came out the victor over overwhelming odds, but these cases were few and far between.
when you get one ship in combat with many, you have a very one-sided battle. Of course, there were instances during the war when a single combatant came out the victor over overwhelming odds, but these cases were few and far between.
Usually, when one lone ship came upon a flight of enemy planes, the solitary plane made a decided effort to duck out. A pilot who was seen streaking for home with a flock of Germans on his tail was never considered a coward. On the contrary, he was thought to be displaying a lot of good common sense. Foolhardy exposure never drew praise.
On this month’s cover, we have illustrated an air battle which, at first glance, looks like a victory for the enemy. A Britisher who was trapped between two Huns got nothing but sympathy and prayers from nonparticipating onlookers, if the combat happened to be taking place over Allied soil. If the Germans were viewing the fight, the Britisher didn’t get even that much of a break. But in our cover, the British pilot is fooling them all, whether they be enemy or Allied bystanders.
Diving full upon a German scout, the British pilot is just ready to line up his target when he suddenly becomes aware of the fact that another German is bearing down upon him from behind. His first impulse is to abandon the prey before him and attempt to get away. He almost carries out his impulse, but in a second he foresees the possible outcome of the battle if he sticks where he is. He is taking a long chance, and he knows it. The only alternative is almost certain defeat.
Having decided that he has a fifty-fifty chance of disposing of these Huns one by one, the British pilot pulls up closer onto the tail of his adversary. The German ship which is bringing up the rear also pulls up closer, but the Hun finds himself in a fit of indecision. There is a chance that he can fire upon the Allied ship before him and register a hit with the first burst. But if he misses, the chances are ten to one that his comrade ahead will get it in the neck. What to do?
Then, suddenly, he sees it is too late to do anything. The British pilot has opened fire, and one short burst proves adequate to knock the German out of the sky.
As his ship falls away in a spin, the remaining German is blinded with rage. Why hadn’t he drilled this British pilot when he had a chance? He has been duped, and, as a result, his comrade has fallen to his death. Now the only thing left is revenge.
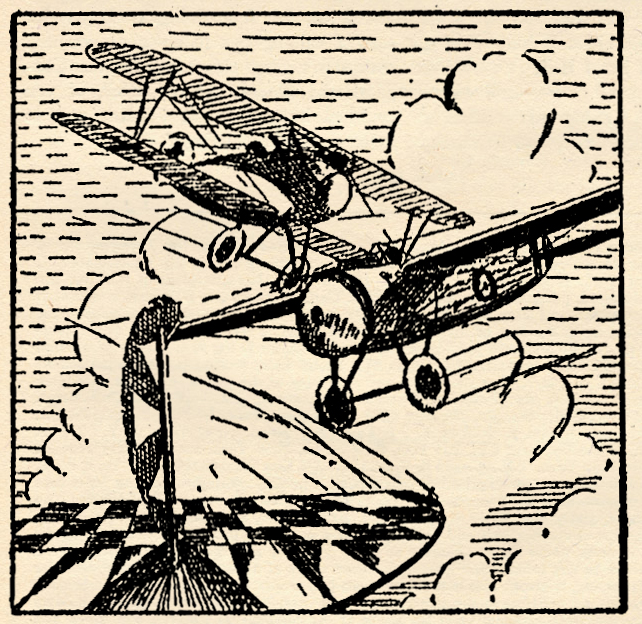
But the Britisher is as wary as he is smart. As soon as he sees that his bullets have found their mark, he spins away from the remaining Hun with the speed of lightning. And now he finds himself free to engage the enemy on even terms.
But what is this dropping out of the clouds on his left? A whole flight of enemy scouts! The Britisher knows when he has had enough. Losing altitude quickly, he gains speed and streaks for home.
Thus a victory is won. An Allied pilot has fought bravely and smartly, and when the odds mount too heavily against him, he quits. A courageous but cautious airmanl
The planes on the cover this month are high-performance single-seater fighters, one of which is comparatively unknown.
The Bristol monoplane was built late in the war by the British and Colonial Aeroplane Co., Ltd. Incorporated in its design are found what was then the latest ideas in airplane construction. As can be seen, it is a high-wing, wire-braced monoplane. The fuselage is circular in construction, the shape of the cowling being preserved down to the tail by fairing. The ship is powered with a 110-horsepower Le Rhone engine, and a large spinner is fixed to the propeller boss. The ship has a top speed of 130 m.p.h.
The German planes pictured on the cover are the well-known Albatross D-3’s.

Sky Birds, February 1935 by C.B. Mayshark
(Combat Maneuvers of War-Time Pilots: The Story Behind This Month’s Cover)