“The Sopwith Triplane” by Robert H. Rankin
Frederick Blakeslee painted all the covers for the entire run of Dare-Devil Aces. And each of those covers had a story behind it. This time, we have more of the approach he used for the covers he painted for Battle Aces—telling us about the ship on cover. But, instead of Mr Blakeslee telling us about the ship on the cover, we have Mr. Robert H. Rankin, formerly a draughtsman for the Fokker Aircraft Corp telling the story of the Sopwith Triplane—featured on the cover of the July 1935 cover of Dare-Devil Aces. . . .
 Editor’s Note: This month’s cover shows what would happen if a certain invention, had been perfected during the War. The rear-pit man in the all metal Junkers is operating a huge, highly magnified tense, so constructed as to concentrate a powerful percentage of the sun’s rays. When focused on the fabric covering of an airplane, this sunlight beam would cause a tiny burn. It is based on the same principle as that of lighting a fire by focusing sunlight on a small glass dial. The Allied ships on the cover are Sopwith triplanes.
Editor’s Note: This month’s cover shows what would happen if a certain invention, had been perfected during the War. The rear-pit man in the all metal Junkers is operating a huge, highly magnified tense, so constructed as to concentrate a powerful percentage of the sun’s rays. When focused on the fabric covering of an airplane, this sunlight beam would cause a tiny burn. It is based on the same principle as that of lighting a fire by focusing sunlight on a small glass dial. The Allied ships on the cover are Sopwith triplanes.
The Sopwith Triplane
By ROBERT H. RANKIN
Formerly draughtsman, Fokker Aircraft Corporation
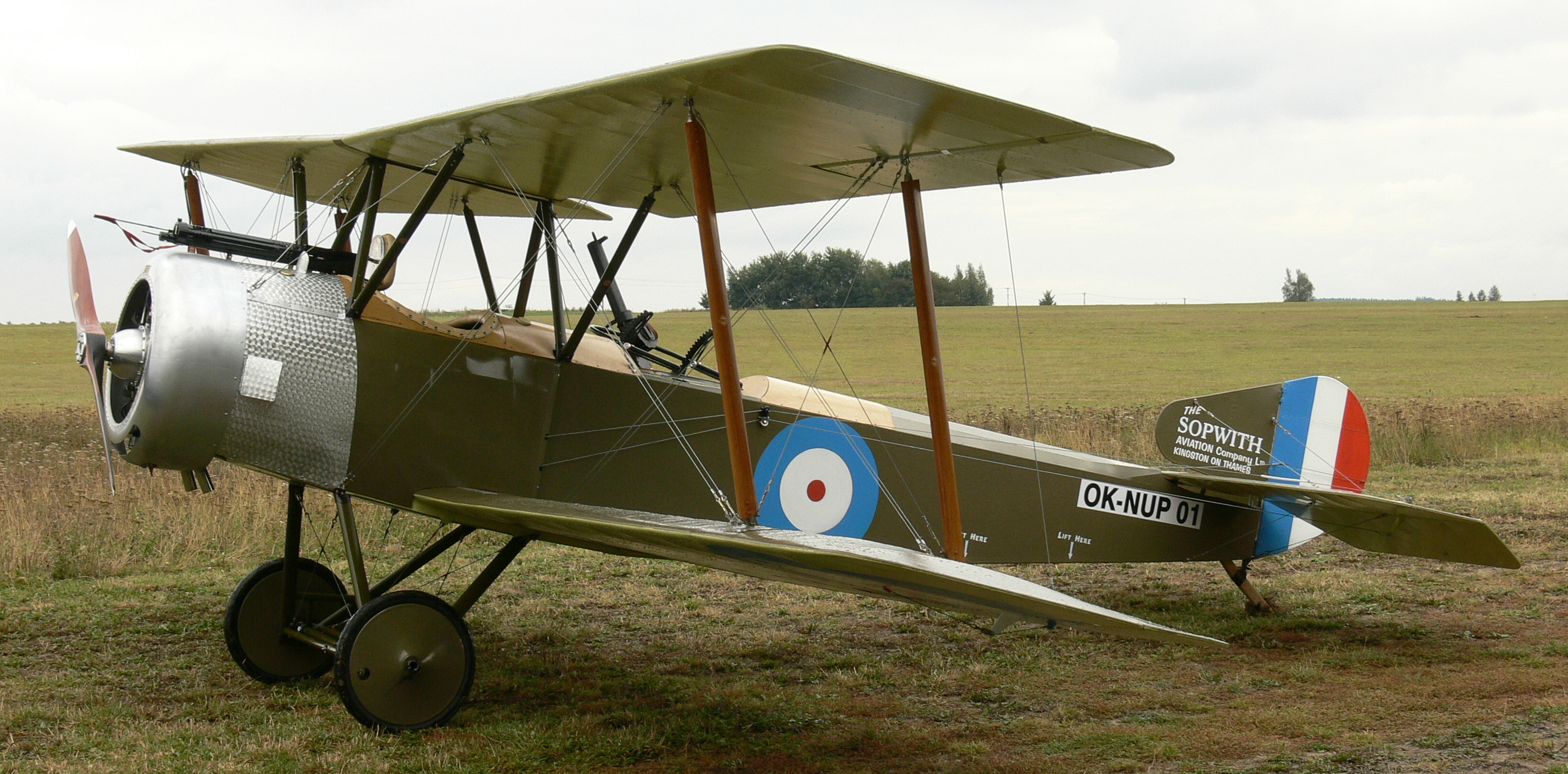
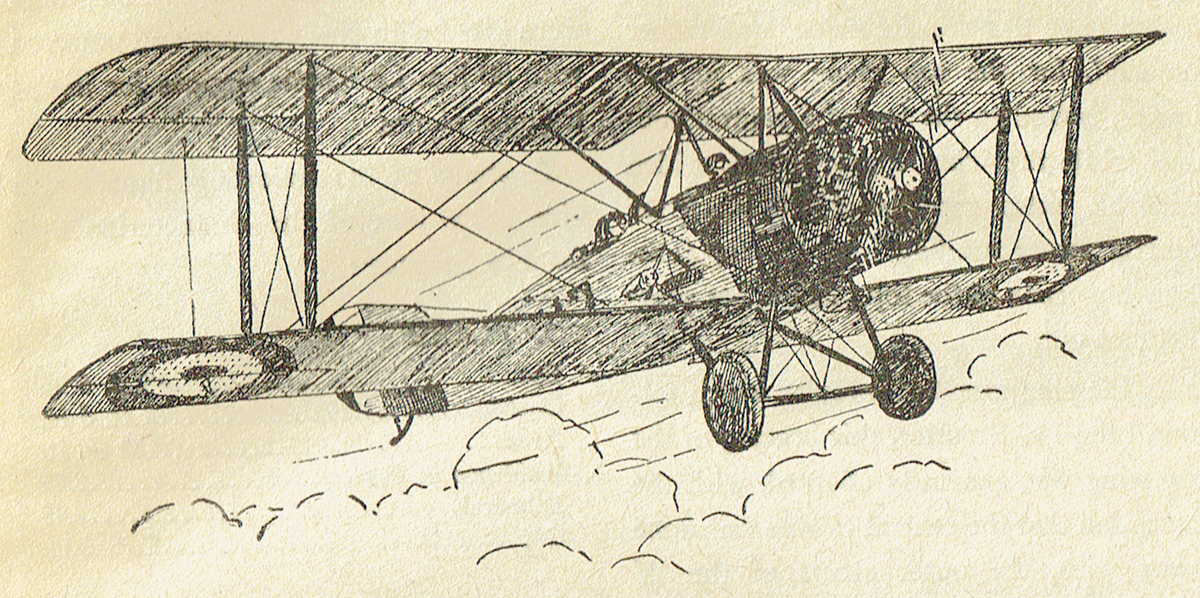
OF THE various Sopwith planes, all of which attained great fame, none is more interesting and characteristic than the Triplane—or as it was better known by the German and British pursuit pilots, the “Tripe” or “Tripe-hound.”
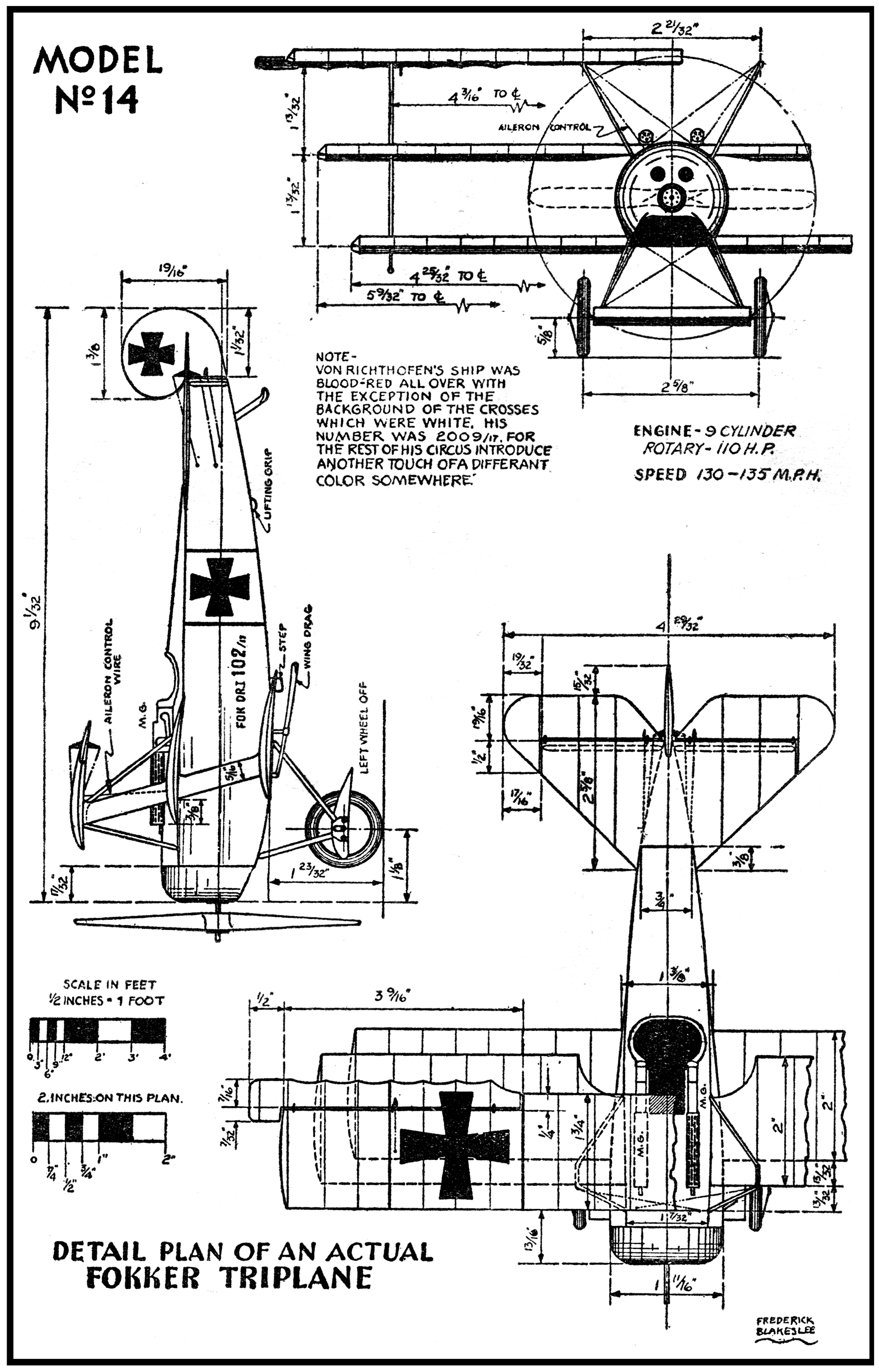
The Triplane was the ninth type produced by the Sopwith works, being accepted by the Experimental Board about four months after the Sopwith Pup. The principal object aimed at in the design of the Triplane was the attainment of an extra high degree of visibility, or in other words, the reduction to minimum of the pilot’s blind angle.
With his eyes on a level with the intermediate plane the pilot had practically an junrestricted arc of vision through some 120 degrees, while a section cut out of the intermediate wing enabled him to have a rather good view of the ground while landing the ship, the position of the cockpit being such that the bottom wing had no restricting effect on the vision.
The narrowness of the chord made possible by the use of three main planes also enabled the pilot to have an exceptional view upward and to either side—a most important consideration in any pursuit ship. Another object aimed at in the “Tripehound” was an increase in maneuverbility.
It will be seen that due to the narrow; chord the shifts in the center of pressure with varying angles of incidence is smaller than in a biplane, and consequently a much shorter fuselage can be used to suport the tail surfaces. In addition to this, the small span of the triplane reduces the moments of inertia in the horizontal plane and an airplane is thus obtained which is very sensitive to its controls, which fact adds to its ability to dodge to various strategic positions in a fight.
The factor of the movement of the center of pressure enabled single I-struts to be used instead of the usual pairs, one springing from each spar. This simplified construction by permitting a simplification of inter-plane wire bracing system. Ailerons of the unbalanced type were fitted to each of the three wings.
The “Tripehound” was armed with a single machine gun mounted on the forward top side of the fuselage. In the hands of experienced pilots the ship gave a splendid account of itself and coped favorably with the Fokkers then in use on the Western Front.
The dimensions of the Triplane follow:
| Sweepback | None |
| Stagger | 1 ft. 6 in. |
| Dihedral (same for each wing) | 2.5 degrees |
| Total wing area | 231 sq.ft. |
| Length over all | 18 ft. 10 in. |
| Overall span | 26 ft. 6 in. |
| Wing span (same for each wing) | 26 ft. 6 in. |
| Chord (same for each wing) | 3 ft. 3in. |
| Wing areas— | |
| Top | 84 sq. ft. |
| Intermediate | 72 sq. ft. |
| Bottom | 75 sq. ft. |
| Gap | 3 ft. |
| Areas— | |
| Aileron | 34 sq. ft. |
| Tail plane | 14.0 sq. ft. |
| Elevators | 9.6 sq. ft. |
| Total | 23.6 sq.ft. |
| Fin | 2.5 sq. ft. |
| Rudder | 4.5 sq. ft. |
| Total | 6.5 sq. ft. |
Powered with a 130 h.p. Clerget engine the Sopwith Triplane had a high speed of 112.5 miles an hour (at 6,500 feet). The landing speed was 35 m.p.h. and it would climb to 6,500 feet in 6.5 minutes and to 15,000 feet in 22.3 minutes.
The plane had a fuel capacity of 180 pounds and a flight range of 310 miles. The ceiling was 20,500 feet. The “Tripehound” weighed 1,103 pounds empty and 1,543 pounds loaded which made a loading of 6 pounds per square foot or 12.4 pounds per horse power.
Although judged by present standards the Triplane was low-powered and rather slow, its speed, ease of handling and general performance were outstanding at the time of its introduction into the Royal Flying Corps.

“The Sopwith Triplane” by Frederick Blakeslee (July 1935, Dare-Devil Aces)





 That sound can only mean one thing—that Bachelor of Artifice, Knight of Calamity and an alumnus of Doctor Merlin’s Camelot College for Conjurors is back—Yes it’s the marvel from Boonetown, Iowa himself—Lieutenant Phineas Pinkham! It was a strange chain of circumstances that pulled Phineas Pinkham right out of France, towed him across the Channel, and finally deposited him in a very bucolic spot in Merrie England.
That sound can only mean one thing—that Bachelor of Artifice, Knight of Calamity and an alumnus of Doctor Merlin’s Camelot College for Conjurors is back—Yes it’s the marvel from Boonetown, Iowa himself—Lieutenant Phineas Pinkham! It was a strange chain of circumstances that pulled Phineas Pinkham right out of France, towed him across the Channel, and finally deposited him in a very bucolic spot in Merrie England.