“Lindbergh—the Lone Eagle” by C.B. Mayshark
THIS May we are once again celebrating the genius that is C.B. Mayshark! Mayshark took over the covers duties for Sky Birds with the July 1934 and would paint all the remaining covers until it’s last issue in December 1935. At the start of his run, Sky Birds started featuring a different combat maneuver of the war-time pilots. Mayshaerk changed things up for the final four covers. Sky Birds last four covers each featured a different aviation legend. “The Lone Eagle” himself was the subject of the penultimate issue of Sky Birds—Charles Lindbergh!
Lindbergh—the Lone Eagle
The Story Behind This Month’s Cover
 A MAN who enjoys the admiration of a hundred and twenty million countrymen; a man whose name has filled the headlines from hemisphere to hemisphere for eight years; a man whose amazing feats of daring have thrilled a world which has long been used to thrills; a man whose unassuming modesty and genuine simplicity have caused his name to be written into the history of the world’s progress; and, most of all, a man who is unalterably a man in every sense of the word—that is Colonel Charles A. Lindbergh.
A MAN who enjoys the admiration of a hundred and twenty million countrymen; a man whose name has filled the headlines from hemisphere to hemisphere for eight years; a man whose amazing feats of daring have thrilled a world which has long been used to thrills; a man whose unassuming modesty and genuine simplicity have caused his name to be written into the history of the world’s progress; and, most of all, a man who is unalterably a man in every sense of the word—that is Colonel Charles A. Lindbergh.
Lindbergh was born in 1902 without, of course, the slightest inkling of what fate had in store for him. But somehow, from the beginning, his career seemed to be guided by the unseen hand of destiny, and bit by bit the experience that was to be invaluable on that history-making day in May, 1927, was accumulated.
Lindbergh made his debut in aviation in February, 1922, when he enrolled in a flying school at Lincoln, Neb. After learning to fly and being unequivocally bitten by the aviation bug, which was pretty much on the rampage around that time, he purchased a U.S. Government Jenny for $500, and his fondest dream was a reality at last.
It seems that this modest young man had ideas in the back of his head and designs in his imagination of such ambitious scope that they needed prestige and a record to lead them along their difficult path. So Lindbergh became a military man by enrolling as a cadet in tho United States Air Service Reserve. He was afterwards commissioned a captain. A short time later, he joined the Missouri National Guard with the rank of first lieutenant, and he was eventually promoted to the rank of colonel.
Lindbergh was in aviation for a serious purpose, and so was not content to drift along, picking up odd jobs here and there and engaging himself in barnstorming trips, as so many other aviators were doing at that time. He wanted to do something which required skill, experience and a sense of responsibility. He made his first flight as an air mail pilot in April, 1926. The air mail service in those days was a pretty risky proposition, and any man who went in for it had to have courage—and plenty of it.
It was during this period that Lindbergh conceived the idea of making a solo trans-Atlantic flight. In the winter of 1927, he persuaded the Ryan Company to build him a ship—the now famous Spirit of St. Louis, and in April of that year, he made a record-breaking transcontinental run from California to New York.
On May 20th, Lindbergh took off on the flight that was to be one of mankind’s greatest accomplishments. Very few people realize the skill and courage and physical condition that were essential to the success of that flight, but whatever it took, Lindbergh had in abundance, and the most amazing part of the whole thing was that his modesty wouldn’t permit him to believe that he had done something which warranted all the congratulations and back-slapping that were showered upon him from the far corners of the earth. Regardless of what his realizations were, he came home in glory to the resounding acclaim of not only America, but of the whole world.
Upon landing in this country, he made arrangements to make a tour of America under the auspices of the Daniel Guggenheim Fund for the promotion of aviation, and it is estimated that he visited seventy-five cities.
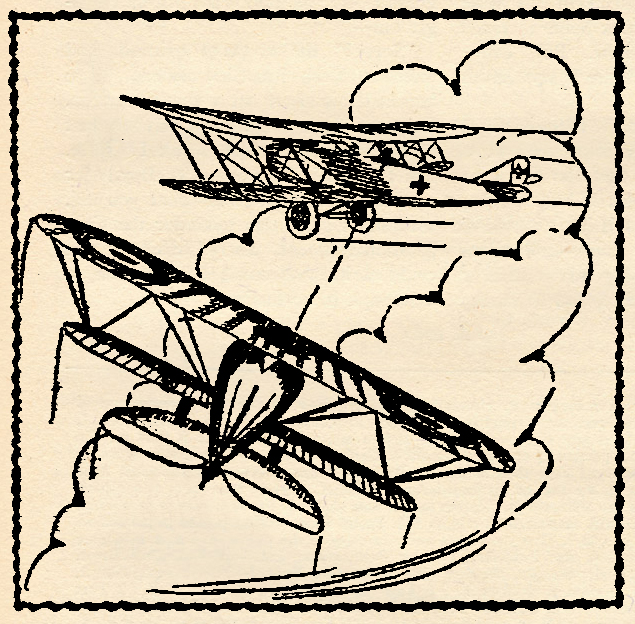
Lindbergh is the ranking member of the mythical Caterpillar Club, having upon four occasions resorted to the parachute to save his life. One of these is depicted on the cover, along with a scene from his famous transatlantic flight.
Lindbergh’s decorations include the Congressional Medal of Honor, the Distinguished Service Medal, the Distinguished Flying Cross, Chevalier of the Legion of honor (France), Order of Leopold (Belgium), and several others.

“Lindbergh—the Lone Eagle” by C.B. Mayshark
Sky Birds, September 1935