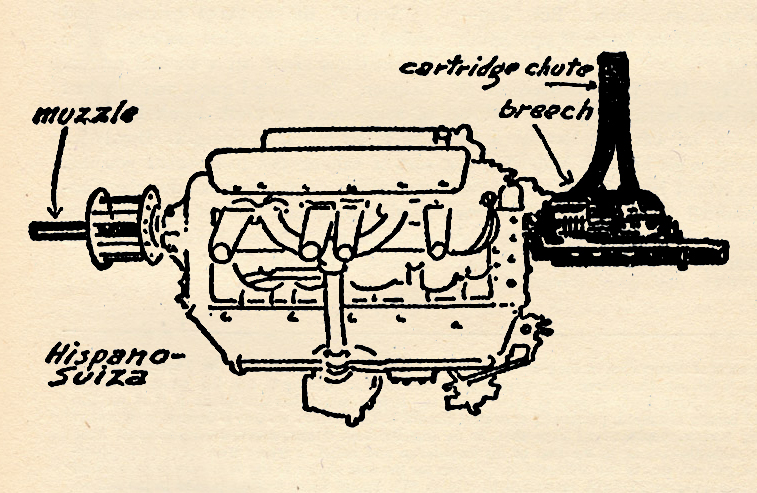
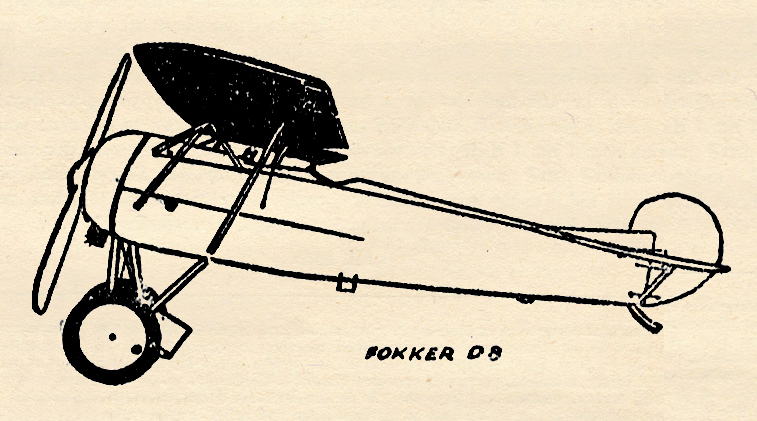
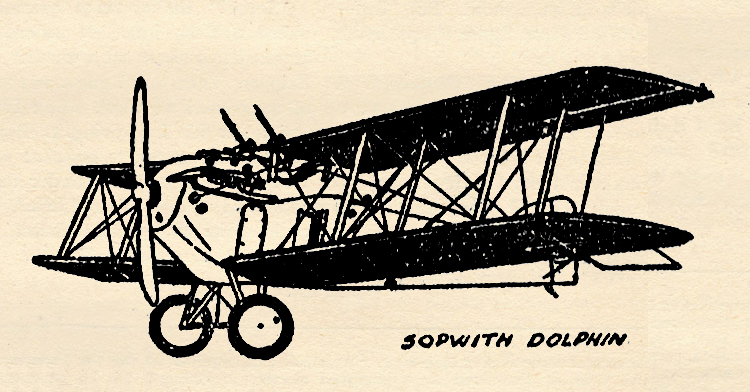
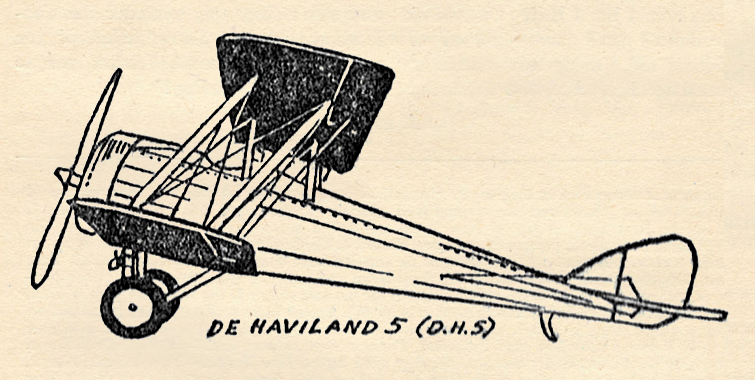
“The Lone Eagle, February 1934″ by Eugene M. Frandzen
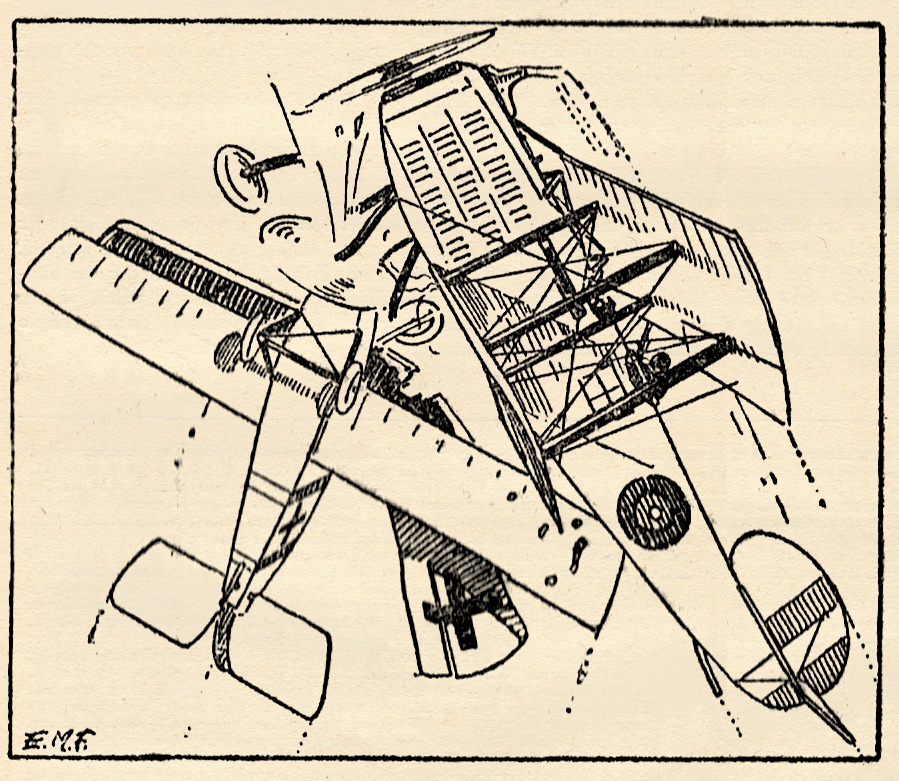
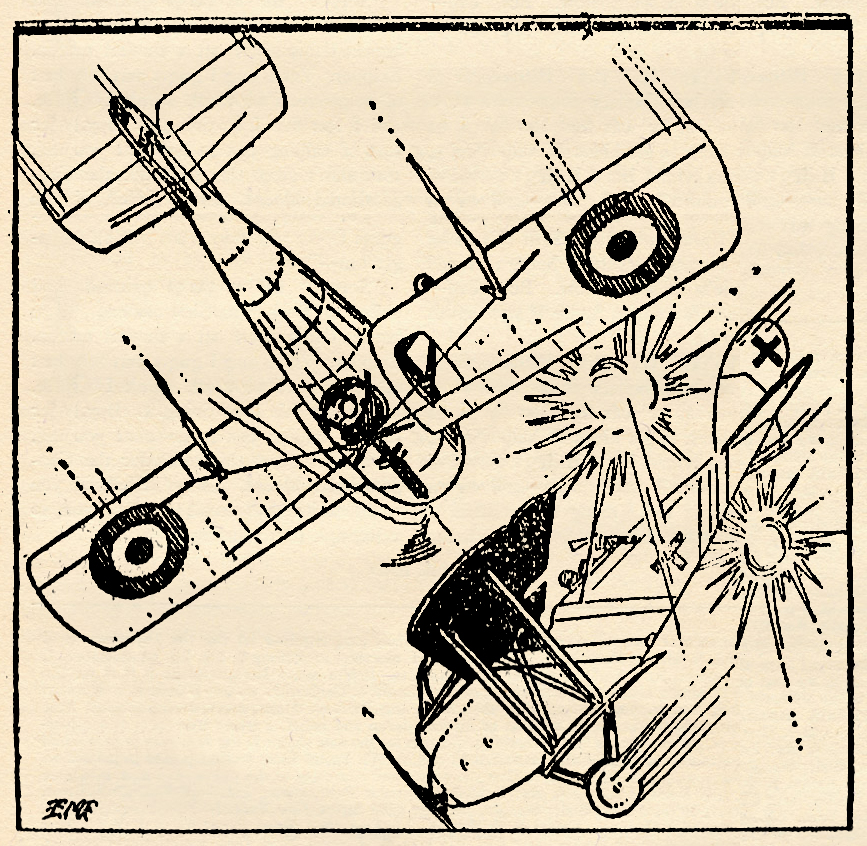
Eugene M. Frandzen painted the covers of The Lone Eagle from its first issue in September 1933 until the June 1937 issue when Rudolph Belarski took over with the August issue of that year. At the start of the run, Frandzen painted covers of general air action much like his Sky Fighters covers. Here, for the February 1934 issue, Frandzen has a British Bristol monoplane taking on a cornered German L.V.G.!
The Story of the Cover
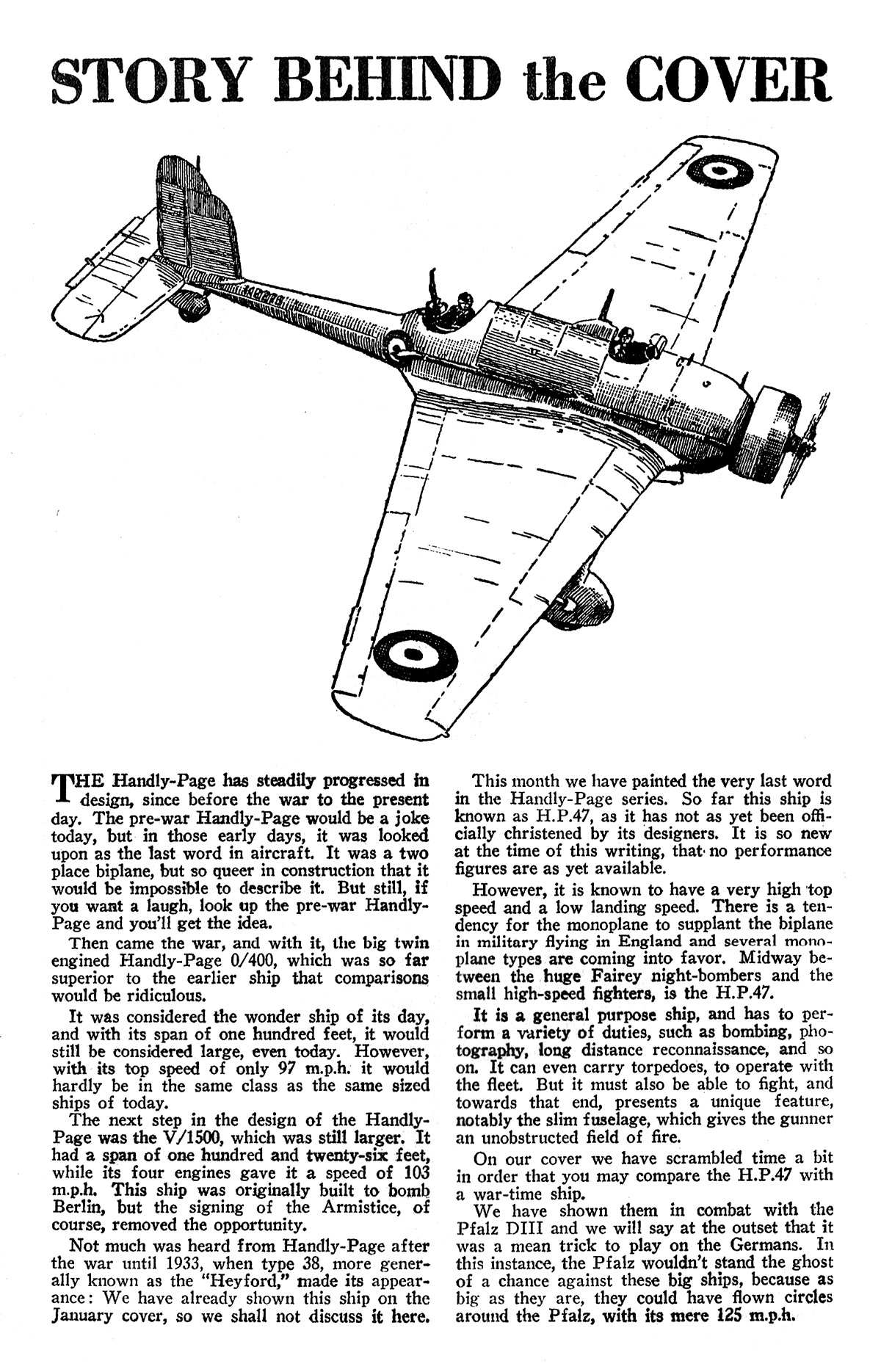
THE planes pictured on this  month’s cover are the Bristol monoplane, one of the prettiest little jobs turned out by the famous British and Colonial Aeroplane Co. The German ship is an L.V.G. type C.V.
month’s cover are the Bristol monoplane, one of the prettiest little jobs turned out by the famous British and Colonial Aeroplane Co. The German ship is an L.V.G. type C.V.
High above the ground, against a background of blue, these two planes have met. The German pilot was heading back into German territory when the prowling Bristol pilot hopped the German. The Bristol, only rating one gun, was outclassed in armament at the start of the scrap by the L.V.G. which had two guns in perfect working order; one Spandau up front and a Parabellum at the back pit.
For ten or fifteen minutes the two guns on the L.V.G. have kept the Bristol at bay, but the L.V.G. being the slower and bulkier of the two has been more or less driven into maneuvers by the Bristol. And after each maneuver the German has found himself closer to the Allied lines. Also he has been forced to allow his ship to lose considerable altitude.
Over No Man’s Land
They have passed over No Man’s Land with its writhing lines of battered trenches and shell-torn fields. The Allied pilot signals the German to land—gives him to understand that he will be given a safe passage to the ground. The reply from Fritz and his observer is an assorted spray of slugs.
“O.K.,” the Allied pilot yells. And slamming the gas into the hungry carburetor he starts to really do his stuff.
The Bristol slashes back and forth across the back of the L.V.G. like a fighting shepherd dog ripping the hide from a bulldog’s back. In and out of ring-sights— short bursts—few of them, but effective. The German observer shudders, claws at his chest and stiffens, then slumps against the ring of his pit, mortally wounded.
Little Chance of Escape
The German pilot knows now that his tail is unprotected; his chances of escape amount to very little. Still, that small chance is better than nothing. He kicks his ship around and blasts at his enemy, his Spandau hammering out sizzling slugs.
Far below, carefully hidden from keen-eyed Boche airmen, a battery of Yank anti-aircraft guns have been trained on the aerial combatants.
Suddenly the commanding officer sees the Bristol dive away from the spurting gun of the German plane.
“Fire!” barks the artillery officer.
The drone and roar of the fighting planes is drowned by the sharp bark of the “75s.”
The Bristol pilot coming out at the top of a loop sees two blossoms suddenly burst on either side of the L.V.G. He pours a steady stream of lead into the German plane.
An Exciting Moment
That is the spot in the fight pictured on the cover; just that one moment when the unlucky German is beautifully bracketed by a couple of archie bursts and is getting a broadside from the Allied Vickers gun. One second later the German raises his hands above his head. The Bristol closes in on his tail. The anti-aircraft guns cease firing.
“Just in time for lunch, Fritz,” chuckles the victor. He points toward a cleared space flanked by tent hangars far below. The German nods solemnly, shrugs his shoulders—and obeys orders.

The Lone Eagle, February 1934 by Eugene M. Frandzen
(The Story of The Cover Page)