The Lone Eagle, December 1938 by Eugene M. Frandzen
Eugene M. Frandzen painted the covers of The Lone Eagle from its first issue in September 1933 until the June 1937 issue when he would share duties with Rudolph Belarski. At the start of the run, Frandzen painted covers of general air action much like his Sky Fighters covers, shifting to covers featuring famous aces at the end of 1935. For the December 1938 issue, Frandzen gives us a throwback cover with the Pfalz D3 vs the Nieuport 17!
The Story of the Cover
SLEEK, lithe bodies shaped like  bullets and colored with hues of the rainbow, ripped across the battle-scarred sky. New to each other, these strange creatures of prey flew at each other’s throats in an effort to find a vulnerable spot by which the destruction of either might be meted out to the other.
bullets and colored with hues of the rainbow, ripped across the battle-scarred sky. New to each other, these strange creatures of prey flew at each other’s throats in an effort to find a vulnerable spot by which the destruction of either might be meted out to the other.
Cautious maneuvering; a burst of machine-gun spray to warm a death dealing firing arm; a loop; a roll in position; a burst of fire that achieved nothing for either; all these in an effort to prove that each new and strange sky bird was the master of the situation—the new hellkite that would clear the skies of the enemy.
Jerry in his new skyfighter, the Pfalz D3, has a job to perform. The Oberst is warned of French troop concentration in the sector and is ordered to send a man aloft to ascertain the exact position and extent of the movement.
A careful search over the camouflaged terrain five thousand feet below achieves his objective.
Ten kilometers behind the French lines he sees blue-uniformed troops massing to enter the Front lines. Fresh reinforcements are readied to relieve a much battered, half-starved, sleep-wearied line of men; men who are so tired and worn out from the ceaseless barrages of German gun-fire, that they have little left with which to fight back.
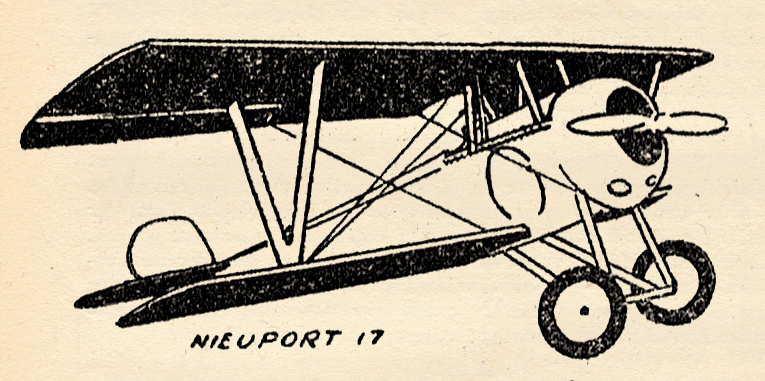
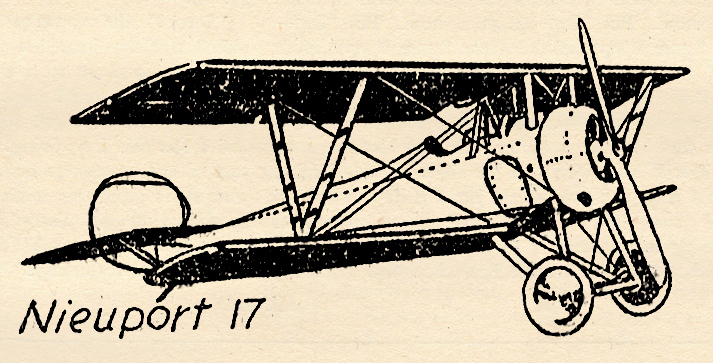
The Nieuport 17
Jerry is satisfied that he has the information German Intelligence requires. He turns toward his own lines—but finds his way cut off. The French had seen him, guessed his mission and sent their newest, sleekest contribution to Allied Air fighters into the sky, the Nieuport 17.

Carefully Frenchy maneuvers for he knows the ship under him. Desperately Jerry makes a bold dash for his lines for his orders are not to engage in combat but to bring his information back.
A burst of Vickers fire rips into the vitals of the Pfalz and it quivers frantically from the shock. Jerry is forced to fight to save himself—and his information. A lunge at the Pfalz and more Nieuport gun-slugs tear at the tail section of the German plane. This time the Jerry turns and fights. But too late. There is a blind spot in his dive. For a moment he cannot see the Nieuport just in front of him, but that moment spells eternity for the desperate man.
A right side slip brings the fast Nieuport into position; a pressure on the thumb grips, and both guns answer with a rocking, flaming spurt of steel that rips into the German plane—and the engine and pilot are silenced—forever. Slowly, in a flat spin, it drops to earth. Once again Nieuport has sent a victor into the skies—and the French troop movement remains a secret.
Light, Fast Planes
Both the Nieuport 17 and the German Pfalz D3 were light, fast, sturdy little planes that had what it takes to give any enemy a real fight. Born of a long line of grand fighting ships, the Nieuport 17 was a single-seater with the parasol idea of construction so sought after by French designers; large upper wing, with very little lower wing. It could out-maneuver many of the Allied and German ships used at the Front at that time.
Powered by a 120 horsepower Le Rhone, its straightaway speed was remarkable. It was similar in design to others of the Nieuport family in its V strut and general construction characteristic of earlier Nieuports.
The Pfalz D3 was a single-seater scout, meticulously streamlined, and sleek as a greyhound. It answered well to the controls, but a downward glide was bad for forward visibility as the top wing obstructed the view when the pilot sought to fire his Spandaus straight ahead.
The Mercedes 160 horsepower engine, gave it a speed of well over 100 miles an hour. German aces became attached to this plane and used it to advantage in their battles against Allied airmen.

The Lone Eagle, December 1938 by Eugene M. Frandzen
(The Story of The Cover Page)