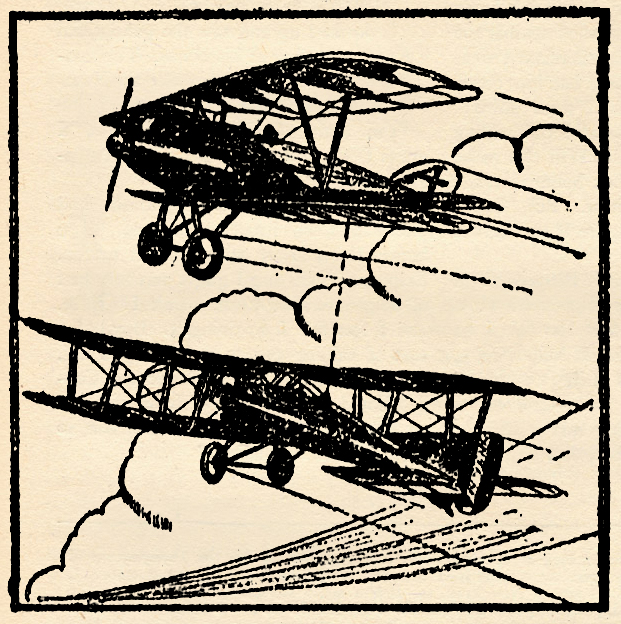
THIS May we’re celebrating the genius that is C.B. Mayshark! Mayshark took over the covers duties for Sky Birds with the July 1934 and would paint all the remaining covers until it’s last issue in December 1935. At the start of his run, Sky Birds started featuring a different combat maneuver of the war-time pilots. The lower corner presenting a play-by-play of that month’s maneuver with the remainder of the cover illustrating it. For October 1934 issue Mayshark gives us “The Camera Crasher!”
Combat Maneuvers of War-Time Pilots:
The Camera Crasher
ONE of the most skilled, daring,  and probably least appreciated members of tho air services during the war was the observer who happened to be capable of using an air camera. Actually, there were very few who could do this job well, in spite of the fact that all airmen were supposed to be trained in the use of the instrument. There was always one man in every squadron who was unlucky enough, right from the start, to be able to get good pictures. From that day on, he was marked.
and probably least appreciated members of tho air services during the war was the observer who happened to be capable of using an air camera. Actually, there were very few who could do this job well, in spite of the fact that all airmen were supposed to be trained in the use of the instrument. There was always one man in every squadron who was unlucky enough, right from the start, to be able to get good pictures. From that day on, he was marked.
The air photographer had to be a strange combination of grim, fighting courage, cool, methodical cunning and unbelievable patience. In the first place, he had to be an observer, a man worthy of any one’s respect. Then he had to be a plodding soul who was game enough to keep his pilot on a straight course while he got strips of pictures to make up the innumerable mosaic maps that the Army seemed to consume with amazing rapidity. Next, he had to be a capable fighting man, in order to do two things at once—and do them both well. He had to be able to fight with one hand on his Lewis or Parabellum gun while with the other he was ramming the plates through the camera with, machinelike precision.
Try holding off two Huns with one hand, ramming the feed handle of the camera back and forth with the other, while you count slowly to eight between plate changes— and you get an idea what it was all about. If your pilot got “windy” during the spree and let his ship run slightly off line to dodge the crackling tracer, you arrived back to find that half your plates had been exposed over a section you had taken the day before. Then back you went again, to try it all over.

The photography proposition was a serious business in the war days. The areas involved had to be photographed regularly, and not just in single shots, as most air-story readers believe. You had to get eighteen plates in a row at a time. The single plate exposure of some particular pinpoint came now and again, but not often enough to make up for the hair-raising experiences getting the mosaic strips.
Then there was the other side of the photography game—the defense against it. This is where we got the idea for this month’s cover.
Here we see a German two-seater that has sneaked over the French lines and caught an important strip which may or may not have considerable bearing on a coming offensive. That ship must be stopped. It must never get back to Germany. But it has already nailed the picture, and there is but one thing to do.
To shoot it down might help, but you cannot be sure. You might kill both the pilot and the observer, and yet the camera plates might still be intact. Then, if they are recovered from the wreckage and developed, they can still do the damage the French feared.
It was to this end that several countries on the Allied side of tho line worked on the development of a cannon-plane, or a ship that was armed with a one-pounder for a particular purpose. That purpose was the same for which Buckingham ammunition was intended—destruction by fire. When a ship was shot down in flames, everything aboard, including cameras and plate boxes, was usually consumed by fire.
The Spad-Cannon is well known, mainly because it was used with fair effect by both Fonck and Guynemer. The real truth of the matter, however, is that the cannon-ship was actually developed for the purpose of destroying enemy camera ships by setting them on fire. The shell used was a graze-fuse incendiary missile. The Buggatti-Spad shown in the upper portion of this month’s cover was a special two-seater using a Buggatti motor, with barrel-type water and oil-cooling chambers shown beneath the nose. The gun used was a spring-recoil weapon fitted to fire through the propeller-shaft, which was hollow and geared to the two eight-cylinder crank shafts. How many of these ships were built and titled on the Front is not known, but we are presenting it to show just how these much-talked-of cannon-ships were employed.
The Albatros CV shown is also a 1918 type, fitted with a 225-h.p. B.W.F. motor. The upper wing had a span of 41 feet, 6 inches, and the lower a span of 40 feet, 4 inches. The strangely balanced ailerons should be noticed. The unfortunate observer-camera man has ripped his Parabellum out of the Gotha-type gun mounting, a steel post which swivels from a point in the center of the floor, and fits into holes or slots around the ring.

Sky Birds, October 1934 by C.B. Mayshark
(Combat Maneuvers of War-Time Pilots: The Story Behind This Month’s Cover)










 great story from the pen of Ralph Oppenheim. Best known in these parts for
great story from the pen of Ralph Oppenheim. Best known in these parts for 
 exciting air adventure with Rusty Wade from the pen of Frank Richardson Pierce. Pierce is probably best remembered for his prolific career in the Western Pulps. Writing under his own name as well as two pen names—Erle Stanly Pierce and Seth Ranger—Pierce’s career spanned fifty years and produced over 1,500 short stories, with over a thousand of these appearing in the pages of Argosy and the Saturday Evening Post.
exciting air adventure with Rusty Wade from the pen of Frank Richardson Pierce. Pierce is probably best remembered for his prolific career in the Western Pulps. Writing under his own name as well as two pen names—Erle Stanly Pierce and Seth Ranger—Pierce’s career spanned fifty years and produced over 1,500 short stories, with over a thousand of these appearing in the pages of Argosy and the Saturday Evening Post. 


 That sound can only mean one thing—that marvel from Boonetown, Iowa is back causing more trouble than he’s worth! That miscreant of Calamity manages believes he has a sure thing goin’, but overplays his hand andgets not only himself in hick, but practiaclly the whole of the Ninth including the Old Man! It’s a case of “cash-and-miscarry” ala Carbuncle in “Sky Finance” from the pages of the June 1936 Flying Aces!
That sound can only mean one thing—that marvel from Boonetown, Iowa is back causing more trouble than he’s worth! That miscreant of Calamity manages believes he has a sure thing goin’, but overplays his hand andgets not only himself in hick, but practiaclly the whole of the Ninth including the Old Man! It’s a case of “cash-and-miscarry” ala Carbuncle in “Sky Finance” from the pages of the June 1936 Flying Aces!



 posts we have a rare story
posts we have a rare story