“The Sopwith Salamander” by Robert H. Rankin
Frederick Blakeslee painted all the covers for the entire run of Dare-Devil Aces. And each of those covers had a story behind it. Although this looks like it should be in his new series of scrambled time covers, instead we get Robert H. Rankin, formerly a draughtsman for Fokker Aircraft Corp, telling the story of the last of the Sopwith war-time machines—The Sopwith Salamander—from the cover of the November 1935 number of Dare-Devil Aces!
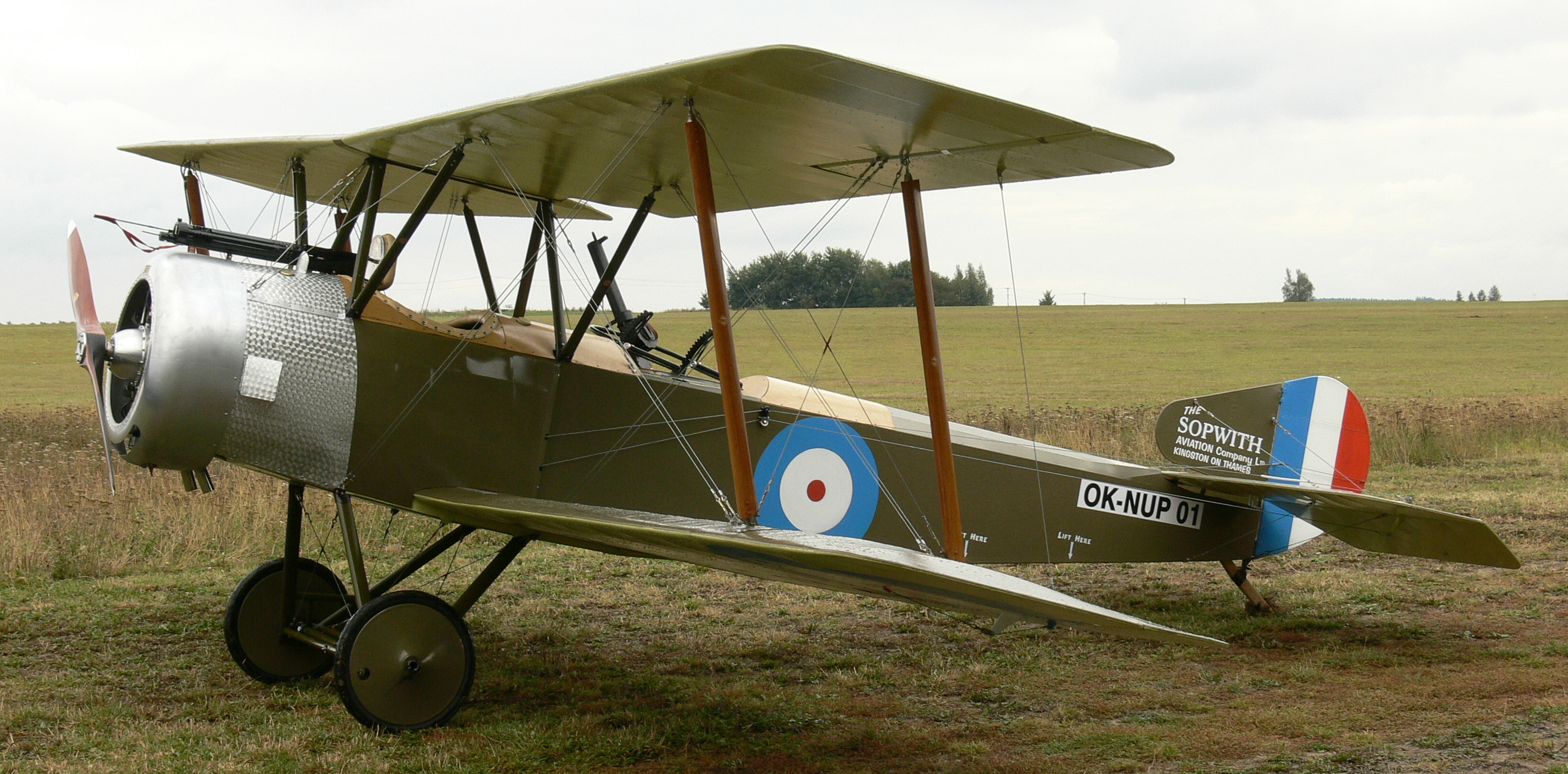
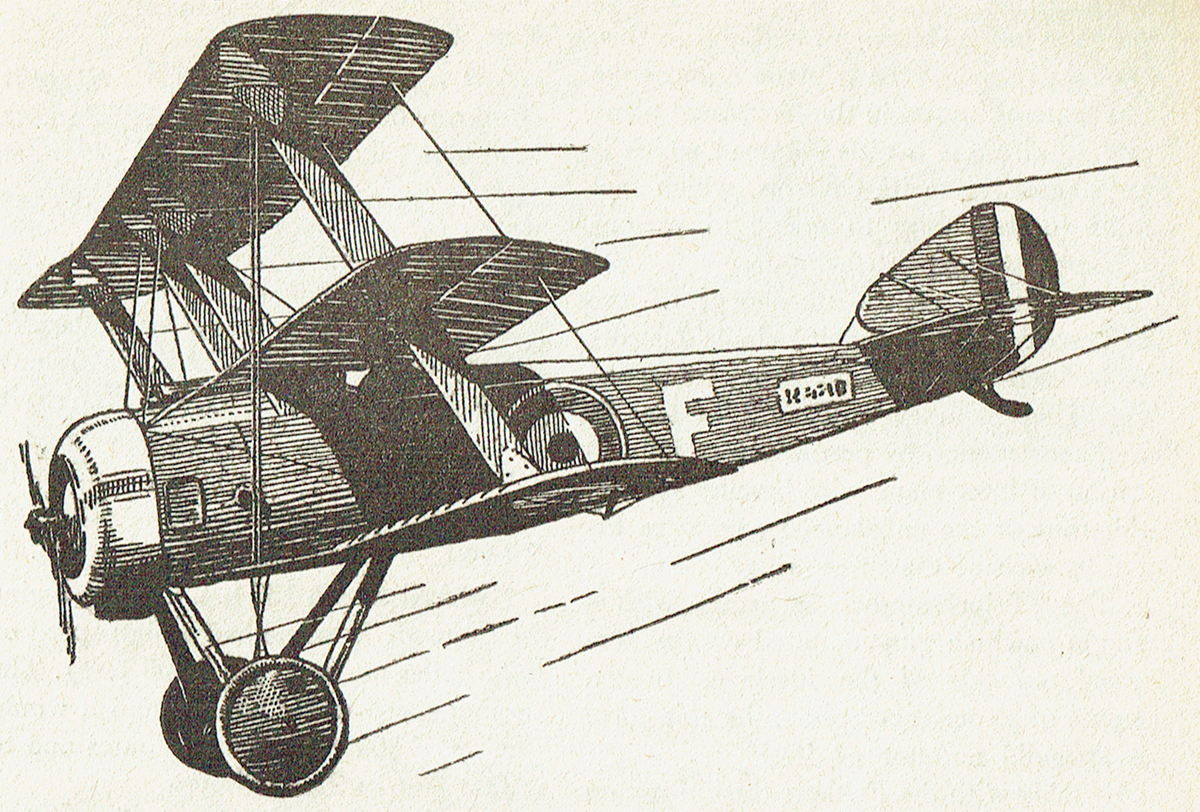
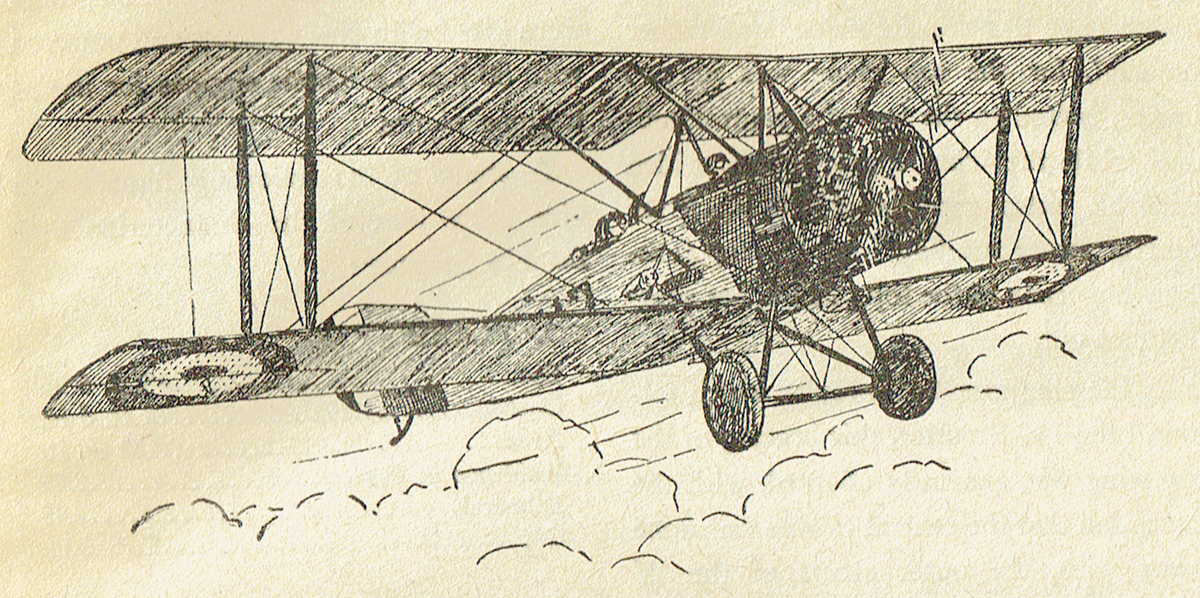
 THE SALAMANDER, the last of the Sopwith war-time machines, was one of the most interesting and efficient types used in the World War. Although the design of the Salamander followed that of the earlier developed Sopwith Snipe, the plane was not intended for use as a scout or fighter—as were the Camel, Pup, Dolphin, and Snipe. It was designed primarily as a trench fighter, and in official circles it was known as the T.F.2.
THE SALAMANDER, the last of the Sopwith war-time machines, was one of the most interesting and efficient types used in the World War. Although the design of the Salamander followed that of the earlier developed Sopwith Snipe, the plane was not intended for use as a scout or fighter—as were the Camel, Pup, Dolphin, and Snipe. It was designed primarily as a trench fighter, and in official circles it was known as the T.F.2.
The rudder of the Salamander was larger than those on the majority of the Sopwith designs. The pilot’s head, owing to the extremely deep fuselage and comparatively small wing gap, was on a level with the top plane, the center of which was partly slotted and partly cut away, to insure a better vision.
Due to the rather large diameter of the engine used, a B.R.2., the rectangularity of the fuselage was apparent toward the tail only, with the result that the fuselage was of a more circular cross-section than was the case in the other Sopwith ships.
Perhaps the mast interesting feature of the Salamander was the manner in which it was armored. Light steel plating formed the front of the fuselage from a point immediately in the rear of the engine, and extended to a point slightly to the rear of the cockpit. This armor, instead of being added to an existing fuselage frame, was a definite structual part of the frame work, and in itself formed the front portion of the fuselage. Thus, the armor plating served a structual, as well as a protective function.
Another variation from the usual Sopwith designs was incorporated in a tapering spine which served to taper off the pilot’s head and at the same time act as a head rest. This spine, being bulletproof, gave the pilot considerable protection against a rear attack.
The total weight of the armor in the Salamander totaled to some 650 pounds, and in addition to this weight, more than 2,000 rounds of ammunition was carried. In all, the ship weighed 2,945 pounds, as compared to the 1,959 pounds of the Dolphin, which was considered a rather heavy plane.

The following figures will give some idea of the performance and construction of the Salamander:


| GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS | |
| Type | Tractor Bi-plane |
| Purpose | Trench fighter |
| Engine | B.R.2, 230 h.p. |
| Weights | |
| Loaded | 2,945 lbs. |
| Empty | 1,844 lbs. |
| PERFORMANCE | |
| Speed (High—at 6,500 ft.) | 123 m.p.h. |
| (High—at 10,000 ft.) | 117 m.p.h. |
| Climb | 10,000 ft. in 17 min. |
| Landing speed | 60 m.p.h. |
| Ceiling | 14,000 ft. |
| DIMENSIONS | |
| Length, over all | 19 ft. 6 in. |
| Stagger | 1 ft. 5 in. |
| Sweepback | None |
| Top Wing | |
| Span | 31 ft 2â… in. |
| Chord | 5 ft. |
| Area, not including ailerons | 139 sq.ft. |
| Incidence | 1.8 deg. |
| Dihedral | 4.0 deg. |
| Bottom Wing | |
| Span | 30 ft. 2½ in. |
| Chord | 5 ft. |
| Area, not including ailerons | 123 sq.ft. |
| Incidence | 1.8 deg. |
| Dihedral | 4.0 deg. |
| AREAS | |
| Total wing area, not including ailerons | |
| Total wing, not inch ailerons | 272 sq. ft. |
| Tailplane | 15 sq. ft. |
| Elevators | 11 sq. ft. |
| Fin | 2.75 sq. ft. |
| Rudder | 9 sq. ft. |
| Total aileron area | 51 sq. ft. |
With the weights carried, the machine had a loading of 11 pounds per horse power, or 9.4 pounds per square foot.
As originally designed, the Salamander was armed with two fixed machine guns, but with its development into a general ground strafer, and later into a contact-patrol ship, the armament was increased, first to four guns, and later to six guns. In this later type there were two Lewis guns mounted on the top wing in such a manner that they could be easily drawn back and reloaded by the pilot from the cockpit.
Then, two Vickers were fixed on the top of the cowling, synchronized to fire through the propeller arc, while two Lewis guns, intended for trench strafing work were mounted on the bottom of the cockpit in such a way as to fire through the floor of the fuselage at an angle of about forty-five degrees.
The Salamander was passed by the experimental board of the Sopwith concern in April, 1918, but it was not until considerably later on in the year that the plane reached a production stage. Consequently few of them were in service over the lines.
In the short time that they were in action they showed such a performance record that it is quite probable, had the conflict lasted longer, the Salamander would have been one of the outstanding planes.
It is interesting to note, in connection with the Salamander, that the armored airplane has always been generally accepted as a logical step in the evolution of military planes by aeronautical engineers and designers. In actuality, however, there have been very few armored ships produced, and in fact, it was not until late in the war that any machines of the armored classification appeared.
For the most part, the greater number of the so-called armored planes produced were most inefficient, and in most instances the protective plating was added to the fuselage frame work of a regular pursuit or observation ship, with the result that the total weight of the machine was increased to a point where, powered with the engines then in use, they were sadly underpowered.
The Salamander, however, was designed from the first as an armored fighter, and inasmuch as the armor plating was made an integral part of the structural framework, the weight problem was done away with. This particular Sopwith offered a definite advance over the designs then in use, and it will be interesting to note in just what ways the modern armored pursuits will follow this pioneer model.

“The Sopwith Salamander: The Story Behind The Cover” by Frederick Blakeslee
(November 1935, Dare-Devil Aces)