My Most Thrilling Sky Fight: Lieut. Quentin Roosevelt
Amidst all the great pulp thrills and features in Sky Fighters, they ran a true story feature collected by Ace Williams wherein famous War Aces would tell actual true accounts of thrilling moments in their fighting lives! This time we have American Flyer Lieutenant Quentin Roosevelt’s most thrilling sky fight!
Quentin Roosevelt was born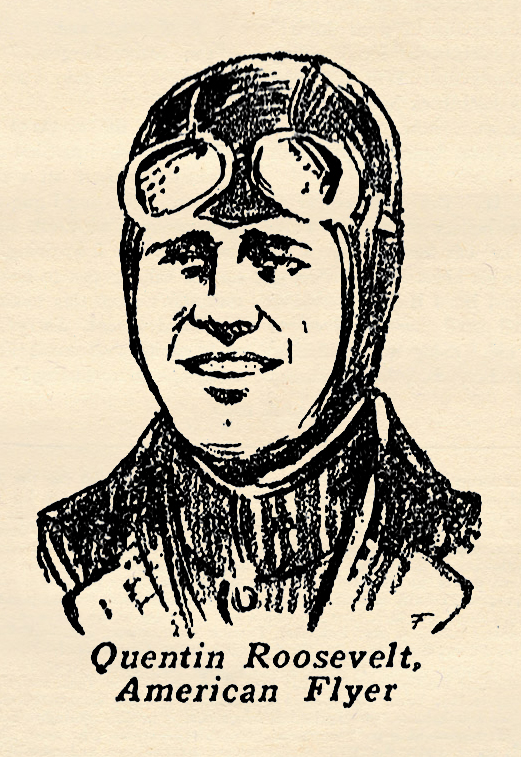  at Oyster Bay, N.Y., the fourth and last son of a famous fighting family, November 19th, 1897, six weeks after his illustrious father, Theodore Roosevelt, had left to fight for the freedom of Cuba. Although handicapped by a permanently injured back, he succeeded by dint of cunning and painful effort in fooling the medical examiners and being accepted for training as an aviator.
at Oyster Bay, N.Y., the fourth and last son of a famous fighting family, November 19th, 1897, six weeks after his illustrious father, Theodore Roosevelt, had left to fight for the freedom of Cuba. Although handicapped by a permanently injured back, he succeeded by dint of cunning and painful effort in fooling the medical examiners and being accepted for training as an aviator.
He was sent overseas July 13th, 1917, and assigned to the 95th Squadron of the First Pursuit Group. From the beginning he gave great promise of becoming a famous Ace—but his promising career was snuffed out before it really began when Sergeant Greber, famous German flyer, conquered him after a terrific battle.
Young Roosevelt died 15,000 feet up in the air. His tiny Nieuport turned over its back, streaked to earth and crashed on a hillside near the little French town of Chamery. He was buried where he fell with high military honors by the Germans. The account below is taken from one of the letters written to his mother.
MY FIRST VICTORY
by Lieut. Quentin Roosevelt • Sky Fighters, September 1935
I WAS cruising on high patrol with my flight when I spied far in the rear of the German lines a formation of seven enemy fighters. Though we were only three I though I might pull up a little and take a crack at them.
I had the altitude and advantage of the sun, and was sure they hadn’t seen me.
I pulled up, got within range, put my sights on the last man and let go. My tracer stream spewed all around him. I saw it distinctly. But for some strange reason he never even turned nor appeared to notice. It was like shooting through a ghost.
By that time the enemy formation began whirling up and down like dervishes. Spandau smoke trails snaked the sky around me and bullets clipped through my wings.
A Web of Fokkers
I stuck with my man, let go again. All of a sudden his tail went up and his ship went down in a vrille, spinning toward the cloud floor 3,000 meters below. I wanted to follow down after him, but his mates had cut me off from my flight and were making it hot on all sides.
I was so far within the enemy lines that I didn’t dare to tarry too long in a drawn-out fight because of my short gas supply, so I fought my way out of the web the Fokkers were spinning about me and ran for home.
Looking back over my shoulder I saw my victim spinning, and he was still spinning when he hit the cloud floor and disappeared. I do not expect to get credit for the victory (my first) because the fight took place too far behind the lines for it to be confirmed.
But, even so, I know now that I am able to hold my place as a pursuit pilot over the front lines.
The Grim War Game
At first I was doubtful, and the first time I was attacked I’ll confess I was scared. But in the heat of the battle I forgot that feeling. It becomes then a sort of grim game, a duel for points, with a victory scored when the opponent dies or is shot down out of control. But one doesn’t have time to think of death when the shooting starts. In the excitement of the moment there is no other thought but getting your sights on the other fellow and letting go with your guns.
I am glad we three took a crack at those German planes—even though we were outnumbered, for it certainly taught me many things. It is experiences of this sort that give one a real thrill.
Yes, to date this has been my most thrilling sky fight. Who knows what will come? In the frenzy of fighting, one never thinks of anything but the battle itself—and a fierce determination to do one’s best predominates over one’s thoughts!
EDITOR’S NOTE: Lieut. Roosevelt’s victory was officially confirmed two days after he was shot down.
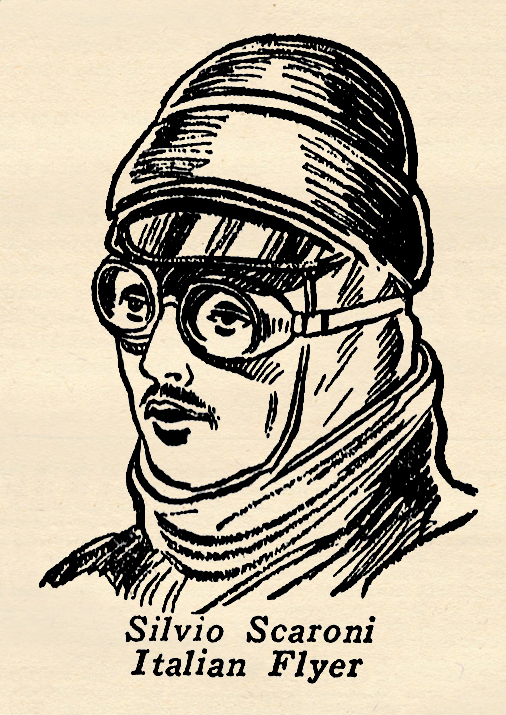




 born at Brescia, Italy, and entered the aviation corps at the beginning of the war. As a bomber he was recognized as one of the best in the Italian Flying Corps and he was very adopt in handling big three-engined Capronis. But the big ships were too slow to satisfy Lieutenant Scaroni. He wanted to fly single Heaters and eventually managed to secure his transfer to a combat squadron on the morning of November 14, 1917.
born at Brescia, Italy, and entered the aviation corps at the beginning of the war. As a bomber he was recognized as one of the best in the Italian Flying Corps and he was very adopt in handling big three-engined Capronis. But the big ships were too slow to satisfy Lieutenant Scaroni. He wanted to fly single Heaters and eventually managed to secure his transfer to a combat squadron on the morning of November 14, 1917.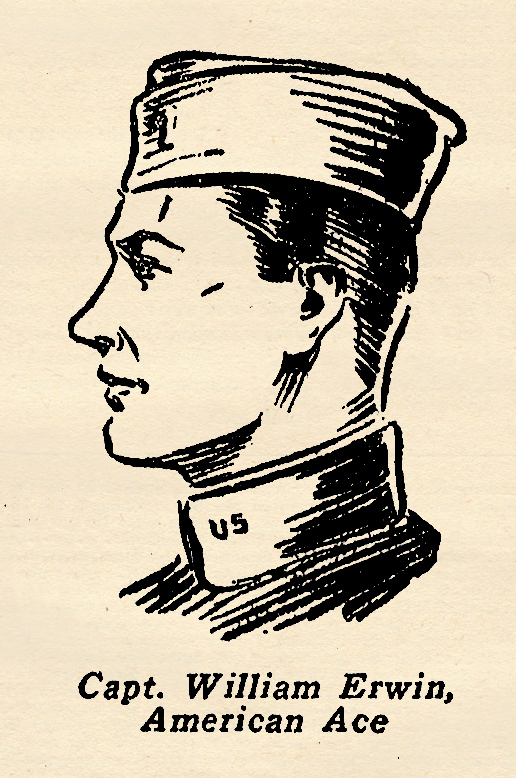 a unique record. He was the only accredited American observation ace, and piled up a string of 9 official victories while flying slow ungainly two-seaters. A Texan, William Erwin enlisted for training the day after war was declared. He received his commission as a Lieutenant after a bare forty hours of flight and was immediately sent overseas and assigned to the First Aero Squadron which he joined on its first day at the front. Before his first week he had downed an enemy plane and the French awarded him the Croix de Guerre. He was awarded additional recognition by the French and also received the American Distinguished Service Cross with Oak Leaves. Through the war safely, without ever having been wounded despite his rare courage and daring, he came to an untimely end while flying the Pacific in a futile search for the missing Dole flyers in 1923. Erwin, himself, recounted the following experience to the compiler of these records on a grey day in the Argonne many years ago.
a unique record. He was the only accredited American observation ace, and piled up a string of 9 official victories while flying slow ungainly two-seaters. A Texan, William Erwin enlisted for training the day after war was declared. He received his commission as a Lieutenant after a bare forty hours of flight and was immediately sent overseas and assigned to the First Aero Squadron which he joined on its first day at the front. Before his first week he had downed an enemy plane and the French awarded him the Croix de Guerre. He was awarded additional recognition by the French and also received the American Distinguished Service Cross with Oak Leaves. Through the war safely, without ever having been wounded despite his rare courage and daring, he came to an untimely end while flying the Pacific in a futile search for the missing Dole flyers in 1923. Erwin, himself, recounted the following experience to the compiler of these records on a grey day in the Argonne many years ago. none is more poignantly remembered than Charles Nungesser, who began his flaming war career as a Lieutenant of Hussars and was one of that famous lighting band of cavalrymen that stopped the German Uhlans at the gates of Paris. For his exploits in this heroic stand he was awarded the Medal Militaire, the highest combat award.
none is more poignantly remembered than Charles Nungesser, who began his flaming war career as a Lieutenant of Hussars and was one of that famous lighting band of cavalrymen that stopped the German Uhlans at the gates of Paris. For his exploits in this heroic stand he was awarded the Medal Militaire, the highest combat award. air did not fly single-seater fighting planes, and all of the heroes did not accomplish their missions single handed. Some of the great feats were accomplised by the pilots of the bigger, bulkier, clumsier, two and three-seater observation and bombing planes. Sergeant Engmann was one of the heroes of this latter class. Obscure, reticent, retiring by nature, his own part in the many successful missions accomplished by the greatest of all German observation aces, Captain Heydemarck, whose pilot he was, marks him as one of the outstanding flyers of the war.
air did not fly single-seater fighting planes, and all of the heroes did not accomplish their missions single handed. Some of the great feats were accomplised by the pilots of the bigger, bulkier, clumsier, two and three-seater observation and bombing planes. Sergeant Engmann was one of the heroes of this latter class. Obscure, reticent, retiring by nature, his own part in the many successful missions accomplished by the greatest of all German observation aces, Captain Heydemarck, whose pilot he was, marks him as one of the outstanding flyers of the war. the first contingent of flying cadets to be graduated from the air combat school at Issoudun, France, the great flying field established by the American Air Service on foreign soil after the United States entered the war. He was one of tho original members of the famous 95th Pursuit Squadron, the first American squadron to do actual front line duty with the American Army. Among his squadron mates in the 95th were Lieutenant Quentin Roosevelt and Lieutenant Sumner Sewell.
the first contingent of flying cadets to be graduated from the air combat school at Issoudun, France, the great flying field established by the American Air Service on foreign soil after the United States entered the war. He was one of tho original members of the famous 95th Pursuit Squadron, the first American squadron to do actual front line duty with the American Army. Among his squadron mates in the 95th were Lieutenant Quentin Roosevelt and Lieutenant Sumner Sewell. of the least known, but nevertheless, one of the greatest and most successful of the German war birds. A nobleman by birth, he was educated for service in the army beginning with his early childhood. When the war broke out he was an officer in the Uhlans, the most aristocratic branch of the German Army. After transferring to the flying corps, he served some time as an observer, before learning to become a pilot himself; paralleling in that respect the career of Baron Manfred von Richthofen, who preceeded him as an officer of Uhlans.
of the least known, but nevertheless, one of the greatest and most successful of the German war birds. A nobleman by birth, he was educated for service in the army beginning with his early childhood. When the war broke out he was an officer in the Uhlans, the most aristocratic branch of the German Army. After transferring to the flying corps, he served some time as an observer, before learning to become a pilot himself; paralleling in that respect the career of Baron Manfred von Richthofen, who preceeded him as an officer of Uhlans. a great war hero when lie transferred from the cavalry to the flying corps. After a short course of just two weeks in flying school, he was sent up to the front again as a bombardment pilot. But flying heavy, unwieldy bombers was too slow and tedious work for him. He was transferred to a single-seater fighting squadron after two months with the bombers. It was then that his remarkable record began to grow.
a great war hero when lie transferred from the cavalry to the flying corps. After a short course of just two weeks in flying school, he was sent up to the front again as a bombardment pilot. But flying heavy, unwieldy bombers was too slow and tedious work for him. He was transferred to a single-seater fighting squadron after two months with the bombers. It was then that his remarkable record began to grow.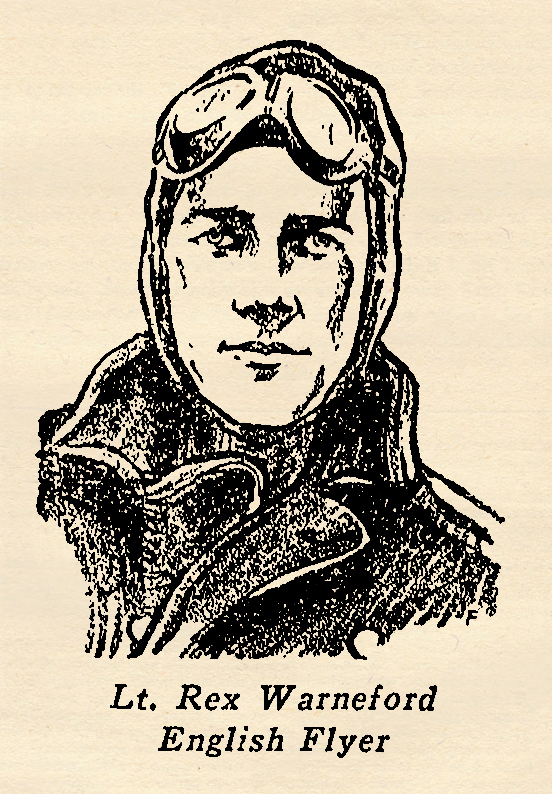 of the British Royal Flying Corps was the first airman to shoot down an enemy Zeppelin, likewise he was the first war pilot to win the coveted Victoria Cross. Previous to his epic fight with the raiding Zeppelin young Warneford was a comparatively obscure pilot. After this amazing and brilliant victory he leaped to the highest pinnacle of fame, he escaped from the German lines with his plane after being forced down fully five miles from his own territory. A troop of German cavalrymen rode up to take him prisoner, but using his machine-gun to the greatest advantage he managed to hold them off until he had completed temporary repairs on his plane. Then, amidst a continual hail of fire, he took off in flight, running the gauntlet of fire successfully, eventually to land within his own lines. Unhappily, two days after the V.C. had been conferred on him, he was killed in an air accident near Paris. In the account below he tells the story of this fight in his own words:
of the British Royal Flying Corps was the first airman to shoot down an enemy Zeppelin, likewise he was the first war pilot to win the coveted Victoria Cross. Previous to his epic fight with the raiding Zeppelin young Warneford was a comparatively obscure pilot. After this amazing and brilliant victory he leaped to the highest pinnacle of fame, he escaped from the German lines with his plane after being forced down fully five miles from his own territory. A troop of German cavalrymen rode up to take him prisoner, but using his machine-gun to the greatest advantage he managed to hold them off until he had completed temporary repairs on his plane. Then, amidst a continual hail of fire, he took off in flight, running the gauntlet of fire successfully, eventually to land within his own lines. Unhappily, two days after the V.C. had been conferred on him, he was killed in an air accident near Paris. In the account below he tells the story of this fight in his own words: the Zeppelin raiders as told by the raiders themselves have come out of the Great War. Captain Ernst Mathy was one of the most famous of all wartime Zeppelin commanders, having made before he was killed in his final raid over London, six successful night raids over that well protected city, more than any other Zeppelin commander. It was Captain Mathy who developed and perfected most of the strategy of attack for the giant Zeppelins operated by the Imperial
 Flying Corps.
the Zeppelin raiders as told by the raiders themselves have come out of the Great War. Captain Ernst Mathy was one of the most famous of all wartime Zeppelin commanders, having made before he was killed in his final raid over London, six successful night raids over that well protected city, more than any other Zeppelin commander. It was Captain Mathy who developed and perfected most of the strategy of attack for the giant Zeppelins operated by the Imperial
 Flying Corps.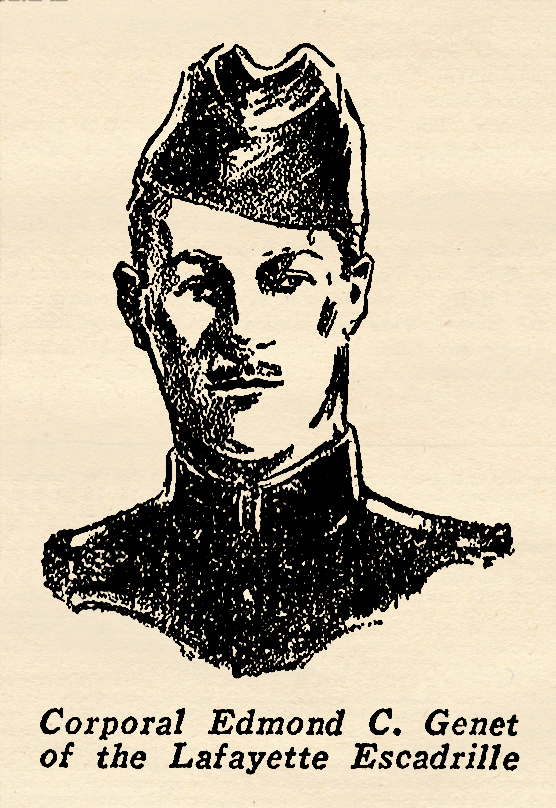 Citizen Genet, who served as the revolutionary ambassador from France during George Washington’s term as president, Edmond C. Genet had a distinguished heritage. Mild-mannered and handsome he was a typical soldier of fortune at heart, possessing an astonishing courage. At 10 he missed an appointment to Annapolis and immediately enlisted in the navy where he participated in the taking of Vera Cruz. A year later he was in battle in Haiti. Later on after the war in Europe broke out, he sailed for France to enlist in the Foreign Legion. He served for some years in the trenches as a simple poilu, then was transferred to aviation and assigned to Escadrille N-124, better known as the Lafayette, where he was the youngest American in a company of famous men. Genet’s flying time on the front was short. He was one of the few airplane pilots to be killed in the air by enemy shrapnel. He was the first American to die in action under the stars and stripes, his death occurring just ten days after America entered the war. The account below is from one of his letters home.
Citizen Genet, who served as the revolutionary ambassador from France during George Washington’s term as president, Edmond C. Genet had a distinguished heritage. Mild-mannered and handsome he was a typical soldier of fortune at heart, possessing an astonishing courage. At 10 he missed an appointment to Annapolis and immediately enlisted in the navy where he participated in the taking of Vera Cruz. A year later he was in battle in Haiti. Later on after the war in Europe broke out, he sailed for France to enlist in the Foreign Legion. He served for some years in the trenches as a simple poilu, then was transferred to aviation and assigned to Escadrille N-124, better known as the Lafayette, where he was the youngest American in a company of famous men. Genet’s flying time on the front was short. He was one of the few airplane pilots to be killed in the air by enemy shrapnel. He was the first American to die in action under the stars and stripes, his death occurring just ten days after America entered the war. The account below is from one of his letters home.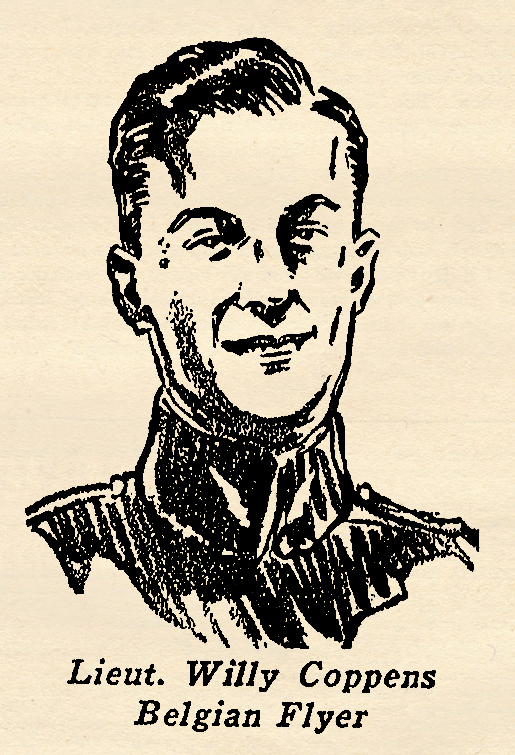 Belgian Ace of Aces. He got his initial training as a soldier and officer in the cavalry division of the army. He transferred later on to the Flying Corps and began immediately to compile the record of victories that gained him top ranking among sky fighters.
Belgian Ace of Aces. He got his initial training as a soldier and officer in the cavalry division of the army. He transferred later on to the Flying Corps and began immediately to compile the record of victories that gained him top ranking among sky fighters.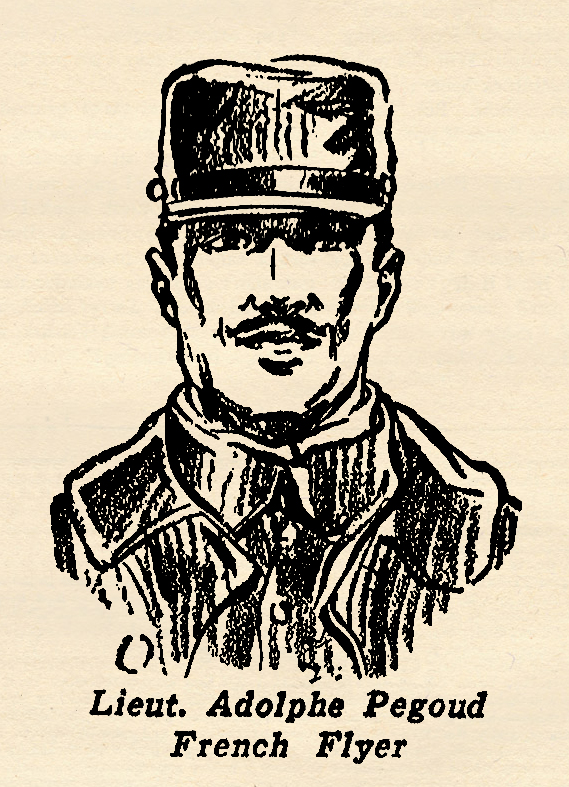 famous flyer before the war began. In 1913, flying a tiny Bleriot monoplane, he astonished the world by doing a series of intricate air maneuvers. Later, he made an upside down landing, the first and to this day the only aviator deliberately to perform such a stunt.
famous flyer before the war began. In 1913, flying a tiny Bleriot monoplane, he astonished the world by doing a series of intricate air maneuvers. Later, he made an upside down landing, the first and to this day the only aviator deliberately to perform such a stunt.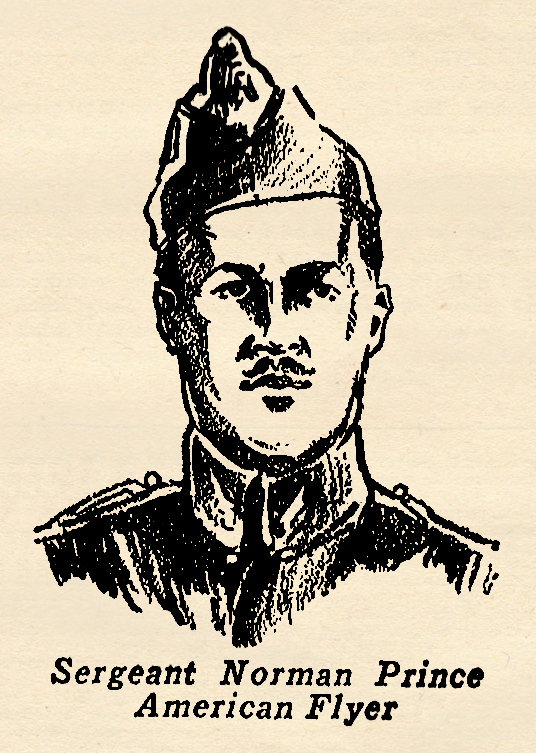 France when the World War began. Being immensely wealthy in his own right, he offered to furnish and equip an entire squadron of planes and pilots. The French Army would not accept this generous offer, but Prince, acting in co-operation with William Thaw of Pittsburgh, convinced the officials that they could muster enough Americans to man an entire squadron. Their offer was accepted, and the LaFayette Escadrille was born. A French officer was put in command. All the rest of the pilots were American. Prince’s death was tragic. Though wounded in an air battle, he managed to fly his crippled plane homeward, and was about to land on his own airdrome in the gathering darkness when his plane ran into a telephone pole and crashed. In his weakened condition he did not have strength enough to guide his plane over or around the obstacle. So perished one of the bravest and most courageous of the early American pilots who gave their lives for France. The story below was told to a French reporter.
France when the World War began. Being immensely wealthy in his own right, he offered to furnish and equip an entire squadron of planes and pilots. The French Army would not accept this generous offer, but Prince, acting in co-operation with William Thaw of Pittsburgh, convinced the officials that they could muster enough Americans to man an entire squadron. Their offer was accepted, and the LaFayette Escadrille was born. A French officer was put in command. All the rest of the pilots were American. Prince’s death was tragic. Though wounded in an air battle, he managed to fly his crippled plane homeward, and was about to land on his own airdrome in the gathering darkness when his plane ran into a telephone pole and crashed. In his weakened condition he did not have strength enough to guide his plane over or around the obstacle. So perished one of the bravest and most courageous of the early American pilots who gave their lives for France. The story below was told to a French reporter.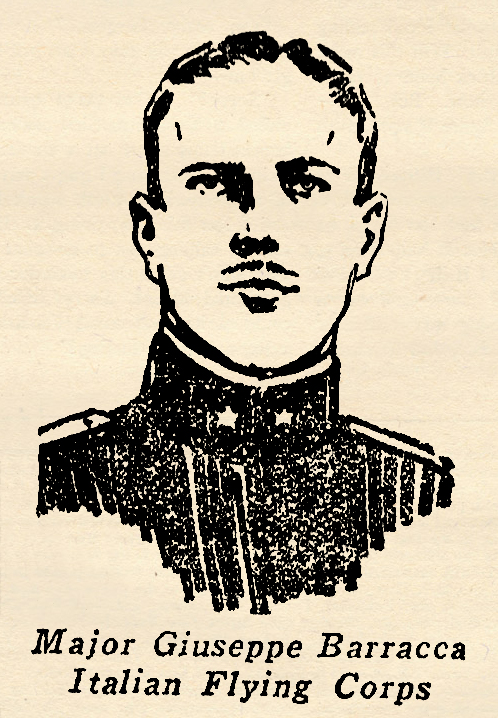 with Alan McLeod of the Royal Flying Corps, who was one of the youngest of the famous flying aces. Major Giuseppe Barracca, Ace of Aces of the Italian Flying Corps, was one of the oldest, being 34 years of age when he was killed in the desperate air fighting above the Piave. Like Captain Ritter von Schleich, he entered the war a cavalry officer, but soon was transferred to the more romantic, yet more hazardous branch of the army, the flying corps.
with Alan McLeod of the Royal Flying Corps, who was one of the youngest of the famous flying aces. Major Giuseppe Barracca, Ace of Aces of the Italian Flying Corps, was one of the oldest, being 34 years of age when he was killed in the desperate air fighting above the Piave. Like Captain Ritter von Schleich, he entered the war a cavalry officer, but soon was transferred to the more romantic, yet more hazardous branch of the army, the flying corps.